- Data: The actual value stored in the node.
- Next: A link, or call it a pointer to the next node in the sequence.
None, signifying the end of the list.
Unlike an array, you can’t access an element in a linked list by its index (e.g., list[3]). To find an element, you must traverse the list from the head node, following the next pointers until you reach the desired node.
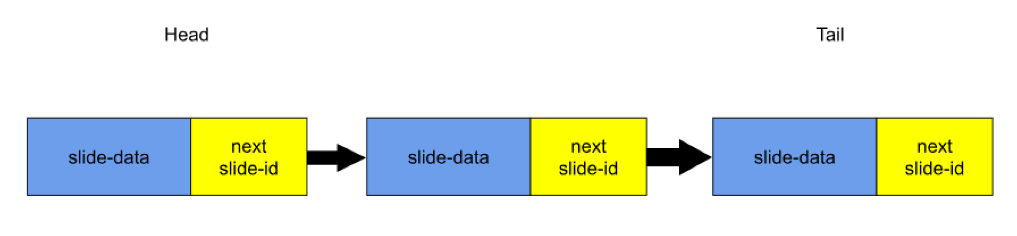
Think of a slideshow where each slide has a “Next” button to go to the following slide. You can only move one step at a time, from the current slide to the next.
This is very similar to a linked list:
- Each slide is like a node.
- The “Next” button acts like a pointer (slide-id) to the next node.
- The first slide is the head of the list.
- The last slide doesn’t link to any other, tail or null .
- If there’s a “Previous” button, it’s like a doubly linked list.
Use Cases
- Implementing other data structures: Linked lists are the building blocks for more complex data structures like stacks, queues, and hash maps.
- Dynamic memory allocation: They are efficient for scenarios where you don’t know the size of the data in advance, as they can grow or shrink dynamically.
- Managing a playlist: A music playlist is a great example. You can easily add a new song to the end or remove a song from the middle without shifting the entire list of songs.

